French Army Signalling System:
Illuminating Fireworks and Other Signaling Devices
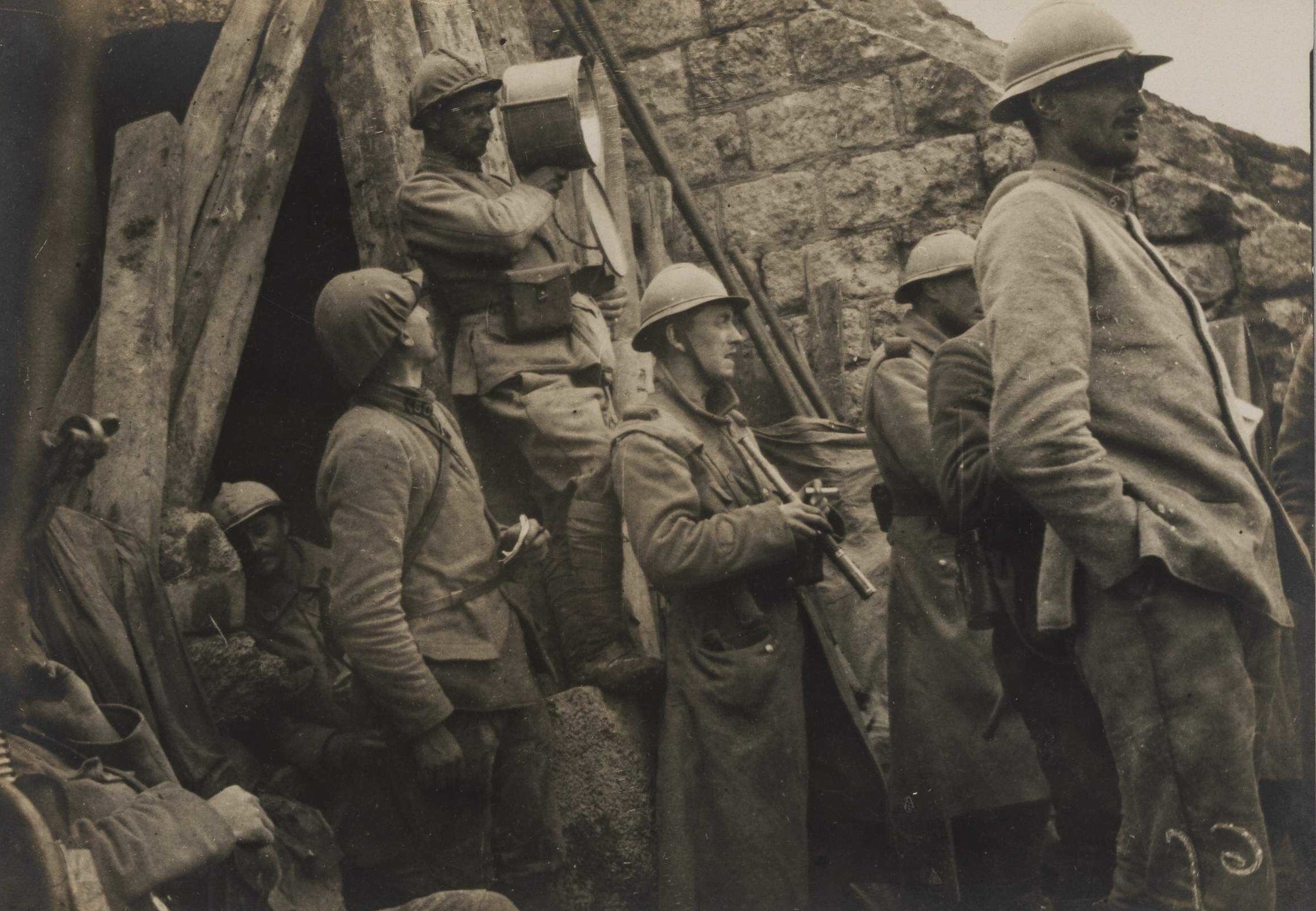

Signal station at Fort Souville, Verdun, July 1916.
Illuminating Fireworks
--34 mm with parachute flare: bursts and deploys parachute at 450 meters (about 10 secs. after departure) 30 sec. burn-time. --Consisting of a shell, a “pot” [the flare], and a directional rod.
Editor’s Note: A 27 mm caliber rocket was also manufactured. It appears in the 1916 manual but seems to have fallen out of use by 1918. It bursts and deploys parachute at 250 meters with a 30 sec. burn-time.
--VB cartridge: fired with a special blank round included with the
cartridge. There are two types:
1)
White flare with parachute – 20-30 sec. burn-time
2)
Star flare – 10 sec. burn-time
--Flare-pistol cartridge (25 mm): white star without parachute – 6 sec. burn-time
--Flare-shotgun (25 mm/caliber no. 4) cartridge: star w/ parachute, bursts at 150m – 30 sec. burn-time.
--Illuminating star (25 mm): flare cartridge without parachute, fired from either a flare-pistol or flare-shotgun – 6 sec. burn-time. It is the most rapid illuminating device which is fired at the least alarm, lighting up instantly and surprising the enemy. The star illuminates about 50 m after it’s departure
--Ground flare composed of cylindrical cardboard covered in black shellac
and paraffined.
--There are three different sizes of white bengales which burn for 3 mins., 1 1/2 min. and 30 secs, respectively. There are also red, green and yellow bengales which have a 30 sec. burn-time.It is lit with a striker which lights a small primer placed at the end of a bickford cord [canon fuse]. In the case of a dud striker, use a match or lighter. The fabrication of spherical shaped bengales with a percussion fuse or pull-pin is being studied.
--Cardboard ball (the size of a tennis ball) –1 minute burn-time. It
is filled with an alumino-thermal composition and fitted with bickford cord. It is lit using a special striker and thrown by
hand.
Editor’s Note: The illuminating grenades appear in the 1916 manual but seems to have fallen out of use by 1918.
Signaling Fireworks and Other Devices
--Signal-rockets are similar to illuminating rockets, except that the signaling “pot” is replaced by a firework, and unlike the illuminating rocket described above, signal rockets are unable to illuminate the ground. Additionally, a smoke pot ignites at the same time that the propulsion composition goes off, which allows the trajectory of the smoke to be tracked. There two main types of rockets: the model 1885 rocket with 13 white or 14 red stars (10 secs.) and the large star model in white, red or green with 6 stars (visible in the daylight). Other types include: caterpillar, yellow smoke, and flag.
--VB signal-flare cartridge: similar to the VB signaling cartridge. 1, 3 or 6 stars in white, red or green with parachute (8 secs.), caterpillar, red or yellow smoke.
--25 mm pistol signal-flare (a.k.a. “military telegraph star”) cartridge: white, red or green with an 8 sec. burn-time.
Note: these can not illuminate the ground.
--35 mm pistol signal-flare cartridge: used in aviation communication; i.e. signaling to planes and observation balloons. The types used were: No. 1. with 1 white star (10 sec. burn-time); No. 2. with 2 white stars (10 sec. burn-time); No. 3. with 3 white stars (8 sec. burn-time); No. 6. with 6 white stars (5 sec. burn-time). All burst at 100 m, 3 secs. after departure.
--25 mm/caliber No. 4 shotgun signal-flare cartridge: flare-adapted model 1874 M 80 Gras rifle and the Mathiot flare-launcher shotgun. Fired same cartridge as the 25 mm flare-pistol.
Tables of Flares and Signaling Cartridges:
|
Flares |
VB Cartridges |
||
|
Large stars: |
White |
Parachute: |
White |
|
Red |
Red |
||
|
Green |
Green |
||
|
― |
1 white star (10
sec.) |
||
|
― |
3 white stars (5-6
secs.) |
||
|
― |
6 white stars (5-6
secs.) |
||
|
Caterpillar (20-25
secs.) |
Caterpillar (20-25
secs.) |
||
|
Yellow smoke (20
secs.) |
Yellow smoke (10-20
secs.) |
||
|
Flag |
― |
||
|
Cartridges: |
Cartridges: |
|
Red (5-6 secs.) |
Red (5-6 secs.) |
|
Green (5-6 secs.) |
― |
|
Flare w/out
parachute (6 secs.) |
1 star (10 secs.) |
|
― |
2 stars (9 secs.) |
|
3 white stars (6
secs.) |
3 stars (8 secs.) |
|
6 white stars (5-6
secs.) |
6 stars (5 secs.) |
|
― |
Caterpillar (20-25
secs.) |
|
― |
Red smoke 10-15
secs.) |
|
Yellow smoke (10-15
secs.) |
Yellow smoke (10-15
secs.) |
--There are two types of bengales: white (which also serves as an illuminating firework) and red. These fireworks are principally used for marking out positions. They burn for 15 or 30 seconds, depending on the model used.
Note: All of the above fireworks, flares, VB cartridges and pistol cartridges are visible during the day and at night with the exception of the smoke (yellow and red) flares and cartridges and the flag-fare, which are only visible in daylight.
--The fireworks signal codes are established by the generals commanding the armies.
Optical Signaling Projectors
--Distribution: 2 per company, 1 per battalion
--The projectors are enclosed in a case containing: extra batteries, extra bulbs (white and red), packets of cotton wadding.
--The 14 cm projector functions and is operated in the same way as the 24 cm projector described below.
--Range: day, 1-3 km; night, 2-6 km
--Distribution: 2 per regiment, 1 per battalion
--This projector is intended to signal: between two ground posts; between the ground and a plane or balloon.
--Range: day, 1500 m to 6 km; night, 3-10 km
--At the service of the regiment to communicate with observation balloons during the day or with artillery.
--Projectors can use red lights in order to distinguish signals from certain apparatuses when necessary. In principal, red lights are reserved for artillery projectors. They also noticeably reduce the range of a projector.
Signaling with Fanions [Signal Flags]
--Distribution: 64 per regiment.
--Dimensions: 50 cm sq.
--Made of cotton canvas, both sides of the flag are half-white and half-red along a diagonal.
Signaling with Panels
--The panels that are used to communicate with planes consist of different models, and their meaning is not fixed in order to maintain security.
a) Identification panels:
--Circular white panels, 3 meters in diameter, serve to identify the division and the brigade. It is usually made up of four 3-meter battens which are joined in the middle by an anchor bolt and terminate with a hook. The canvas panel bears 8 rings that are fitted onto the hooks.
--Half-circle white panels, 3 meters in diameter, indicate a regiment command post (PC).
--Triangular white panels, 2 meters on each side, indicate a battalion command post (PC).
These panels bear black points indicating the number of the regiment and battalion, respectively.
b) Rectangular PC panels: white panel 2 m x 60 cm; 2 per regiment and battalion.
c) Marking panels: panel white on one side and neutral on the other, made of oilskin; 1 for every two men in a company.
**Only use these in the first line. Leave them up only up to the moment when a plane has signaled “understood,” and in any case no more than 15 minutes.
Note: Panels which are white on one side and orange-red on the other are being experimented with.
Summation Table.
|
|
|
Company |
Battalion |
Regiment |
|
Signalers |
NCOs |
― |
― |
2 |
|
2-man |
1 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
Projectors |
14 |
2 |
1 |
― |
|
24 |
― |
1 |
2 |
|
|
35 |
― |
― |
1 |
|
|
Panels |
Identification |
― |
1 |
1 |
|
Rectangular |
― |
2 |
2 |
|
|
Demarcation |
1 per 2 men |
― |
― |
|
|
Pistol-Signalers |
― |
25 |
4 |
|
|
VB Launchers |
― |
3 |
6 |
|